Links to all my PIC tips, tricks and 'mini-project' notes
Whilst the mid-range PIC's can tackle many complex and otherwise almost impossible applications with ease, the challenge is to minimise cost by using the cheapest baseline PIC 'whenever possible'. Baseline PIC's can be had for less than 50p each = I purchased many 16F5x chips for between 40 and 50p each (mainly from CPC as 'remaindered' stock in their 'Bargain bin' section).
The even cheaper to use 12F675 (it has an internal OSC) can be found for as little as 20p (in Qty 10pcs, eBay), as can many other PIC's for less than £1 each. These PIC's are so cheap that you will soon start using them 'for everything' (especially as the PIC can often be used in place of a higher cost 'single function' digital chip - such as divider, ADC, PWM generator etc.) !
Buying the PIC in a 'TSOP' package is (sometimes) cheaper than the DIL/DIP package version = and whilst this costs you 10-20p extra for a mini-PCB TSOP-DIP 'converter', if you use a 'bigger' PCB than the PIC TSOP really needs you can mount other devices (resistors, caps, even osc. crystals) on the same board - and make use of the extra 'pin holes' to wire this up to the rest of your circuit
Below is a mix of programming tips and tricks, common circuit tricks and all the 'mini-projects' I've used the PIC for
I hope these details proves as useful to you as it does to me !
Below, click on the '+' to expand 'in place' (includes diagrams/images) or click the title URL (to view/download the text only version).
(+) 0004 Multi byte ADD - (24bit)
(+) 0005 new PIC 33 instruction set - (macros)
(+) 0006 Binary multiply methods
(+) 0007 8x8 - (multiply)
(+) 0008 8x16 - (multiply)
(-) 0011 Bi color LED driving
Driving a bi-colour LED from one PIC i/o pin
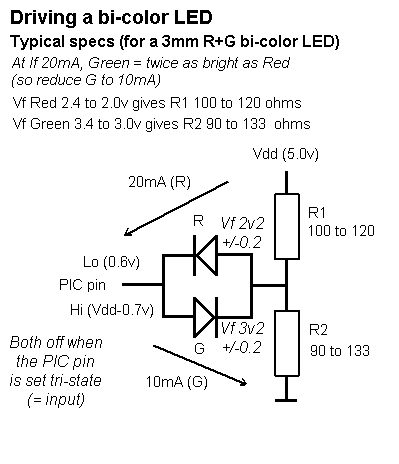
Above circuit is for a typical high Vf Red/Green LED, for other LED colour combinations, see below.
Using a low Vf Green/Yellow LED I paid 5p (actually, 4.8p) each for some "KINGBRIGHT L-937GYW LED, 3MM, GRN/YEL" from CPC (from their 'bargain bin' at Bargain Corner, Electronic & Electrical Components. The relevant specifications are :- Luminous Intensity = Y 8mcd, G 20mcd Forward Current (If) = Y 30mA, G 25mA Forward Voltage (Vf) = Y 2.1V, G 2.2V From the above we note that to obtain the rated brightness we would have to exceed the PIC i/o pin 20mA specification limit. Further, the Green LED is about 2.5x brighter than the Yellow. Since the human eye is more sensitive to Green anyway, the yellow is going to be very hard to see = so 'step 1' is to work out the actual drive currents adjusting for PIC i/o pin limit and light balance. The PIC i/o pin can pull the Yellow LED 'Lo' at 20mA max. reducing it's brightness by 20/30 = approx 5.3mcd. For a similar Green intensity, we reduce the current by 5.2/20 * 25mA = approx 7mA Of course actual light output is NOT a simple linear function of If, however this gives us some 'approximations' Calculating the resistor values We know how much current each resistor must pass, but what will be the voltage drops ? Well, for a typical PIC, we start with i/o 'Hi' = Vcc-0.7 (so 4.3v for a 5.0v supply) and i/o 'Lo' = 0.6v. All we then have to do is subtract the LED Vf to get the voltage dropped by the resistors :- R1, resistor from power (5v) to Yellow LED when i/o pin is Lo (0.6v), will have to pass 20mA and drop (5 - Yellow Vf 2.1 - Pin Lo 0.6v) volts = 2.3v. This gives us a R1 = 2.3/20mA = 115 ohms (I seleted 110 as the 'nearest' E24 value) R2, resistor from Green LED to Gnd when i/o pin is Hi (4.3v), will have to pass 7mA and drop (Pin Hi 4.3v - Green Vf 2.2) volts = 2.1v. This gives us R2 = 2.1/7mA = 300 ohms (a spot on E24 value)
This note last modified: 11th Aug 2017 10:55.